Introduction
The traditional approach to network security has become increasingly ineffective in recent years due to the rise in cloud-based services, remote workforces, and mobile computing. The Zero Trust Security model addresses these challenges by requiring authentication and identity verification for every device and person trying to access resources on a network. In this article, we will explore the concept of Zero Trust Security and its importance in securing digital networks.
Perimeter Security vs. Zero Trust Security
In traditional security models, perimeter security has been the primary means of keeping the network safe from outside threats. Generally, firewalls, network segmentation, and other security measures were implemented to keep external actors out of the network perimeter. However, once inside the perimeter, actors with the right access were given almost free rein of the network.
With the introduction of cloud computing, mobile workforces, and the remote workforce, the perimeter has become more porous, and traditional perimeter-based security measures have become less effective than before. In contrast, Zero Trust Security relies on identity verification and continuous monitoring of user behavior to control access to network resources.
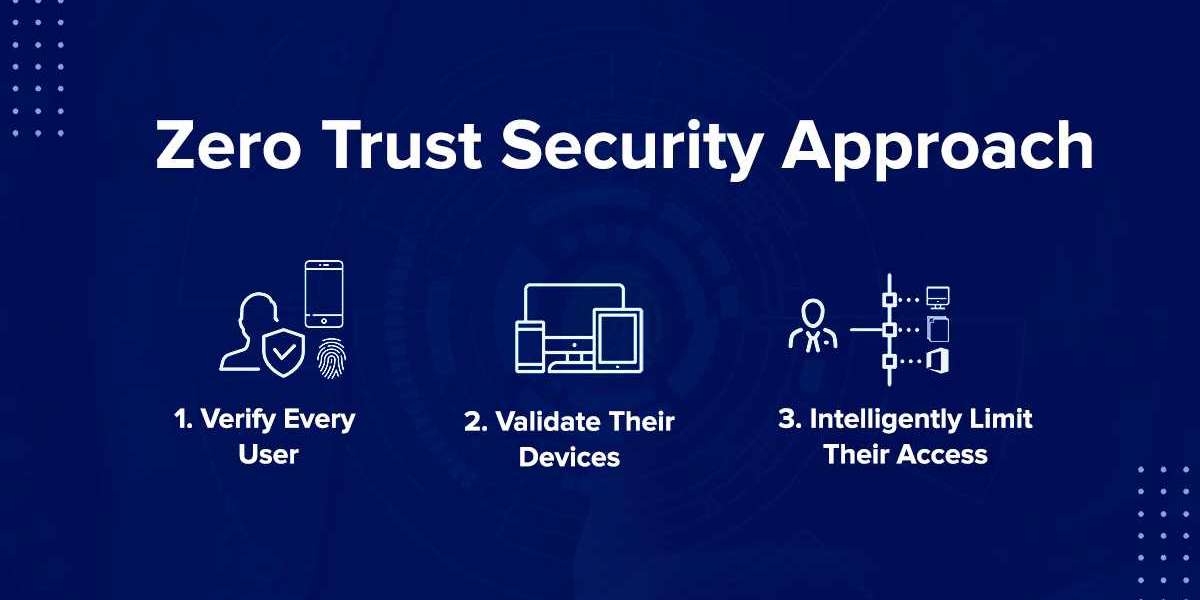
What is Zero Trust Security?
The Zero Trust Security model assumes that every actor, whether inside or outside the network perimeter, trying to access sensitive data or resources is untrusted. This approach essentially flips the traditional security model, where access is granted based on where the actor is, to a model where access is granted based on who the actor is and what access level they have been granted.
Zero Trust Security uses several different techniques to authenticate, verify, and monitor user behavior on the network. The concept of least privilege is central to the Zero Trust Security model, which means each user or device is granted the minimum level of access required to perform the necessary duties. This way, even if the actor's credentials are compromised, access to sensitive data and high-level access is still limited.
Zero Trust Security relies on continuous monitoring of user and device behavior on the network. This allows administrators to maintain visibility over what devices are accessing network resources, and what they are doing while connected. The use of continuous monitoring and behavioral analytics allows administrators to quickly detect and respond to suspicious activities that may present a security threat.
Browse In-depth Market Research Report (111 Pages) on Zero Trust Security Market -
Key Elements of the Zero Trust Security Model
The Zero Trust Security model comprises several key elements which are:
Identity Verification: Verification services help to identify and authenticate users of the network. Zero Trust requires authentication at every access layer, limiting the risks posed by stolen credentials, and ensuring only verified entities have access to network resources.
Network Segmentation: This element partitions the network into smaller chunks